This page calculates the head loss coefficient and head loss at a smooth bellmouth pipe entrance.
The head loss hL can be calculated as:
hL = kloss x (um2 / (2 x g) )
Where kloss is the head loss coefficient, um is the mean flow velocity in the pipe, and g is the gravitational acceleration. kloss is calculated from:
kloss = 235.03x4 - 194.09x3 + 56.739x2 - 7.8163x + 0.50
Where x is the defined as:
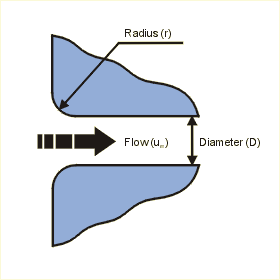
x = r / Dh
Where r is the radius of the pipe and Dh is the hydraulic diameter.
The kloss equation was derived from a curve fit from points when plotted from the following data and are accurate plus/minus 10%:
| r/Dh | kloss |
| 0.00 | 0.5 |
| 0.01 | 0.44 |
| 0.02 | 0.37 |
| 0.03 | 0.31 |
| 0.04 | 0.26 |
| 0.05 | 0.22 |
| 0.06 | 0.2 |
| 0.08 | 0.15 |
| 0.10 | 0.12 |
| 0.12 | 0.09 |
| 0.16 | 0.06 |
| 0.20 | 0.03 |
References
Roberson, John A. and Crowe, Clayton T., Engineering Fluid Mechanics, 2nd Ed., Rudolf Steiner Press, London.1976. p 360 - 384.
Idel'chik, I E. and Fried, Erwin., Flow Resistance, a Design Guide for Engineers, Taylor & Francis, Washington D.C. 1989. p 52.
ASHRAE. ASHRAE Handbook, 1977 Fundamentals, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating And Air Conditioning Engineers, Inc., New York, 1997. p 32.31.