This page calculates the average heat transfer coefficient and plate temperature for an isothermal (constant temperature) flat plate in free stream flow. The convection calculation automatically switches between laminar and turbulent convection correlations based on Reynolds number.
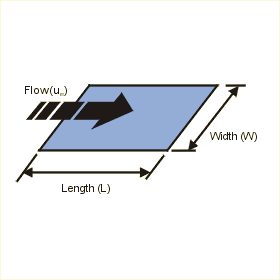
The calculation is based on Nusselt number correlations.
The heat flow (q) from the plate is calculated as:
q = h A x (Tp - Ta)
Where h is the average heat transfer coefficient, A is the area of the plate, Tp is the plate temperature and Ta is the ambient fluid temperature. h is defined as:
h = Nu k / L
Where Nu is the Nusselt Number, k the conductivity of the fluid and L the length of the plate. The Nusselt number is calculated as:
For Laminar Flow - Re < 500,000
Nu = 0.664 Re0.5 Pr0.33
For Turbulent Flow - Re > 500,000
Nu = Pr0.33 ( 0.037 Re0.8 -871)
Where Re is the Reynolds number and Pr is the Prandtl number are calculated using fluid properties as follows:
Re = fluid velocity x Length / kinematic viscosity
Pr = kinematic viscosity / thermal diffusivity
In addition, you must define the fluid properties at the film temperature Tf defined as follows:
Tf = (Tp + Ta) / 2
The above correlations are valid for Prandlt numbers in the range of 0.6 and 50 and are not suitable for low Prandtl fluids like liquid metals and high Prandtl fluids like heavy oils or silicons.
References
Schlichting, H., Boundary Layer Theory, 7th ed., McGraw Hill Book Company, New York, 1979.
Schultz-Grunow, F., Nues Widerstandsgesetz fur glatte Platten Luftfartforschung, vol. 17, p. 239, 1940.
Holman, J.P., Heat Transfer, 7th ed., McGraw Hill Book Company, New York, 1990.